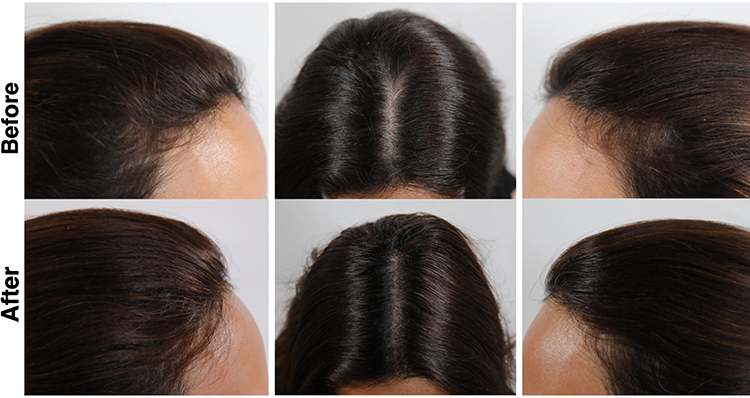
A groundbreaking study by Dr. Shadi Zari, published in the Journal of Stem Cells and Cloning: Advances and Applications, offers new insights into treating telogen effluvium using adipocyte-derived stem cells (ADSCs) conditioned media. Read the full study here.
Understanding Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a form of hair loss characterized by the thinning or shedding of hair, often triggered by various factors such as stress, hormonal changes, or nutritional deficiencies. It occurs when a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting phase, leading to noticeable hair shedding.
The Role of Adipocyte-Derived Stem Cells
Adipocyte-derived stem cells, found in fat tissue, are known for their regenerative properties. The study focuses on the conditioned media from these cells, rich in growth factors and cytokines, which are believed to promote hair growth.
The Study and Its Findings by Dr. Shadi Zari
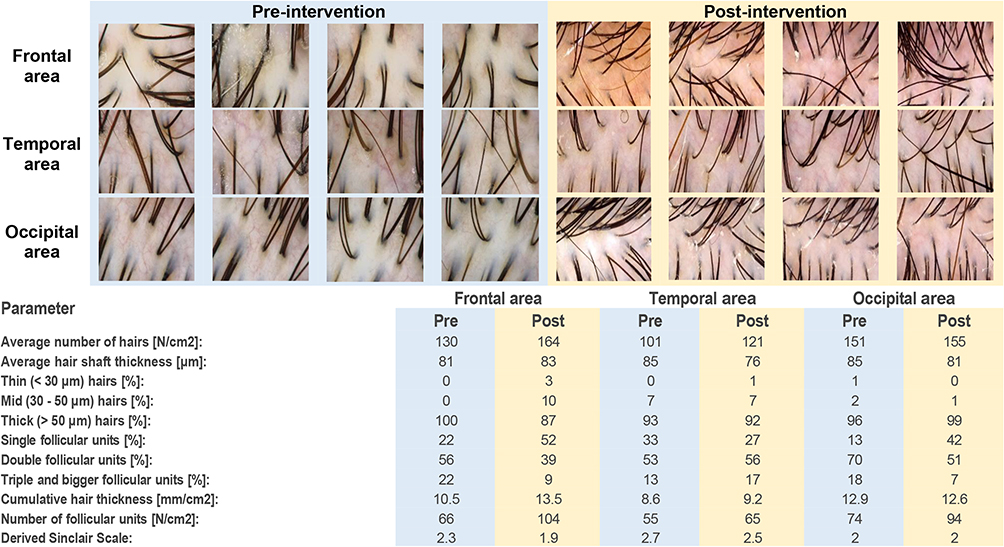
Dr. Shadi Zari’s research involved analyzing the effects of ADSC-conditioned media on patients with telogen effluvium. Key findings include:
- Enhanced Hair Growth: A significant increase in hair density and thickness was observed in patients treated with ADSC-conditioned media.
- Safety and Tolerability: The treatment was safe with no adverse effects, indicating high tolerability.
- Mechanism of Action: The growth factors and cytokines in the conditioned media are thought to stimulate hair follicles, although the exact mechanism is still under study.
Implications for Future Treatments
This study suggests that ADSC-conditioned media could be a non-invasive and effective treatment for telogen effluvium, highlighting the importance of stem cell research in therapeutic development.
Conclusion
The research by Dr. Shadi Zari on adipocyte-derived stem cell conditioned media presents a promising approach to treating telogen effluvium. While further research is necessary, the potential benefits of this treatment are significant. For more detailed information, refer to the original study in the Journal of Stem Cells and Cloning: Advances and Applications. Read the full study here.

