In the realm of dermatologic surgery, a groundbreaking study titled “Beard and Body Hair Transplantation by Follicular Unit Excision Using a Skin-Responsive Device: A Multicenter Study” has emerged as a significant advancement. Published in the esteemed journal, Dermatologic Surgery, this research spearheaded by Dr. Sanusi Umar and his team, including Dr. Raveena Khanna, Dr. Juan Carlos Maldonado, Dr. Kavish Chouhan, and Dr. Alejandro Gonzales, offers new insights into hair transplantation techniques.
The Innovation: Skin-Responsive FUE Device
The study introduces a novel skin-responsive Follicular Unit Excision (FUE) device, designed to address the challenges of conventional nonscalp FUE. This device, known as the Dr. UGraft Zeus FUE device, is adept at handling the varying characteristics of skin and hair, especially in areas with different angles and skin thickness, such as the beard and body.
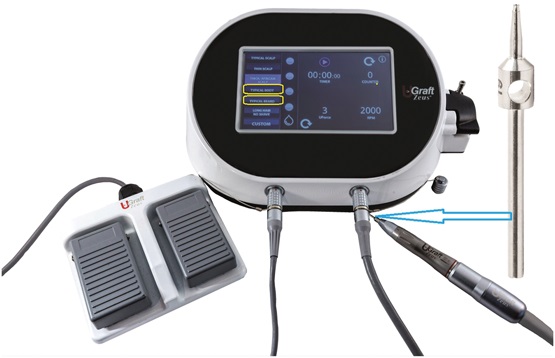
Multicenter Analysis and Findings
Data from four multinational hair restoration clinics across the United States, Colombia, Mexico, and India were analyzed. The study focused on patients who underwent beard and body hair transplantation using the new device. The results were promising, showing a significant reduction in graft transection rates (TRs), which were less than 7% on average.
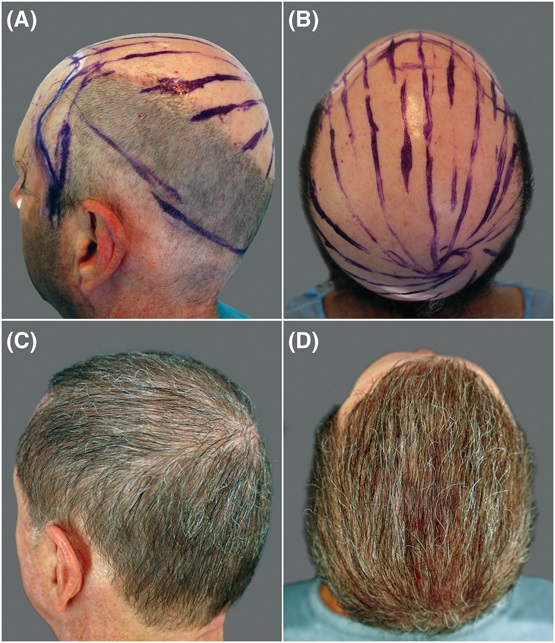
Patient and Surgeon Satisfaction
Patient feedback was overwhelmingly positive, with a majority rating their outcomes as “very happy.” Surgeons also reported an increased willingness to perform beard and body FUE using the new device compared to older techniques.
The Sanusi FUE Scoring Scale
A notable aspect of the study is the Sanusi FUE Scoring (SFS) scale, developed to evaluate the complexity of FUE donor areas. This scale considers factors like skin thickness, firmness, and hair curliness, aiding in the selection of appropriate device settings for optimal results.
Conclusion and Implications
This study marks a significant step forward in the field of hair transplantation. The skin-responsive FUE device not only improves the efficiency and outcomes of beard and body hair transplants but also enhances patient satisfaction and surgeon adoption rates. The multicenter approach and diverse surgeon experiences add robustness to the findings, although the retrospective nature and small sample size are noted limitations.

